Keep life saving antibiotics effective
Use them appropriately in human medicine and not in food production
WHY DOES ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE MATTER?
By the Facts:
When patients have drug-resistant infections and healthcare providers’ first attempts at treatment haven't worked—last resort antibiotics are the only option to save lives. Colistin and a precious few antibiotics are our last line to save lives from drug-resistant infections. But in 2017, a dozen countries admitted to squandering colistin to make animals grow faster. While sick farm animals deserve treatment, antibiotics that are a last-line defense in human medicine should be reserved for patients in our hospitals
Among the World Health Organization’s list of medical important antimicrobials, colistin, quinolones and a few other antibiotics are the highest-priority critically important antimicrobials.
From 2015, the use for colistin in farming is expected to grow by around 5% every year until 2021, when there will be 16,500 tonnes used globally
Some countries already have progressive bans on colistin’s use in livestock for any purpose, but many countries only ban for growth promotion or still allow its export of colistin for non-human use.
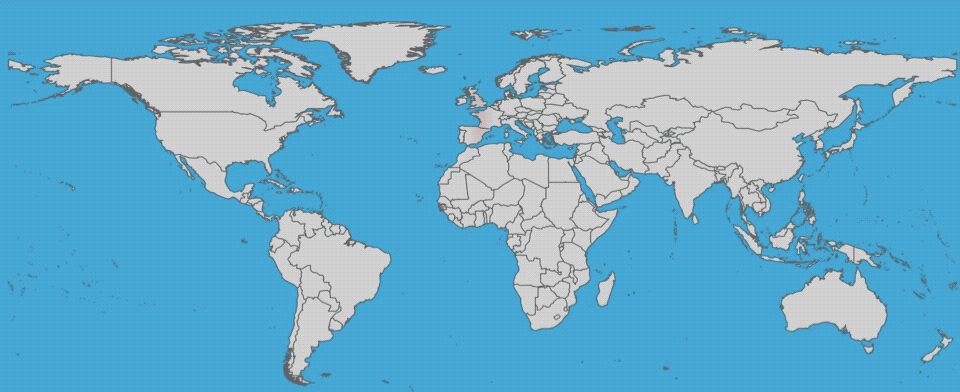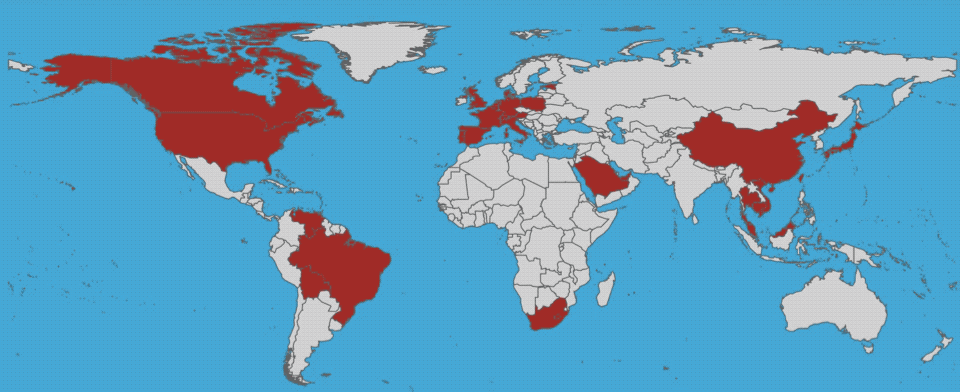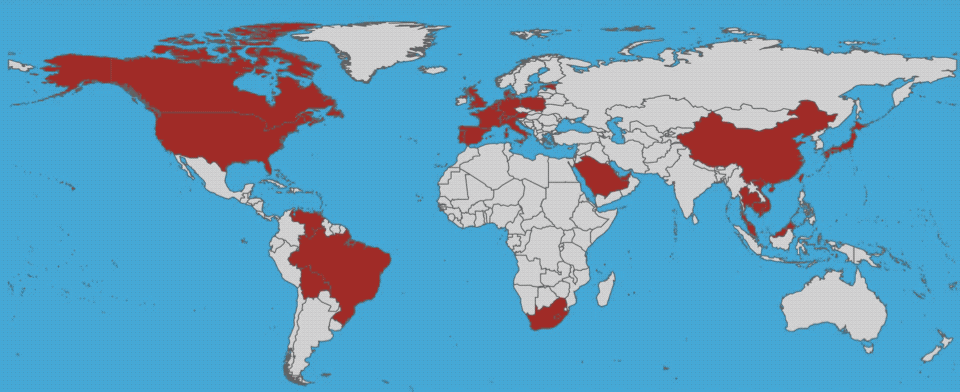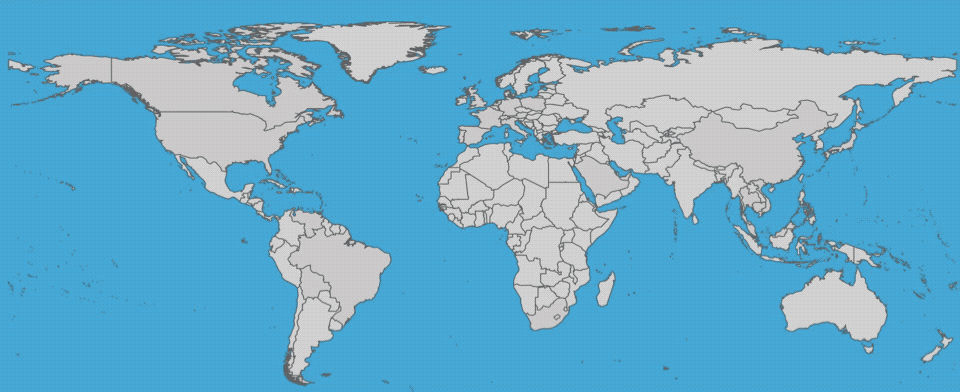
colistin resistance has gone global. TAKE ACTION!
Click to Tweet: Antibiotic resistance is a One Health problem, last-resort antibiotics in animals is a man-made one via @reactgroup
Click to Tweet: Treat animals well … not with unnecessary antibiotics. Routine antibiotic use in agricultural promotes antibiotic resistance, a global threat to health. #HealthForAll #Preparedness #AWorldatRisk via @reactgroup
Data for map from Wang, Ruobing, et al. Nat. Commun. (2018) and used under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Additional resources
Guidelines
Guidelines on use of medically important antimicrobials in food animals (WHO)
Science
Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene MCR-1 in animals and humans in China (Lancet)
Science
The global distribution and spread of the mobilized colistin resistance gene mcr-1 (Nature)
Policy
Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine, 2019 (WHO)
News
China bans colistin as a feed additive for animals (Lancet)
Science
Comparison of different approaches to antibiotic restriction in food-producing animals: stratified results from a systematic review and meta-analysis (BMJ Global Health)
Report
3rd annual report on the use of antimicrobial agents intended for use in animals (OIE)
News
India bans use of "last hope" antibiotic on farms (The Bureau of Investigative Journalism)
Created in 2005 ReAct - Action on Antibiotic Resistance is one of the first international independent networks to articulate the complex nature of antibiotic resistance and its drivers. ReAct was initiated with the goal to be a global catalyst, advocating and stimulating for global engagement on antibiotic resistance by collaborating with a broad range of organisations, individuals and stakeholders.
The IDEA (Innovation + Design Enabling Access) Initiative based at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health seeks to foster innovation and the design of new technologies for greater health access and impact through a combination of research, policy work, and training. It also collaborates with a variety of initiatives across Johns Hopkins University and beyond.
To learn more about our Initiative, visit this post by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
Views expressed on this page do not necessarily reflect those of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.